Goal Representations for Instruction Following – The Berkeley Artificial Intelligence Research Blog
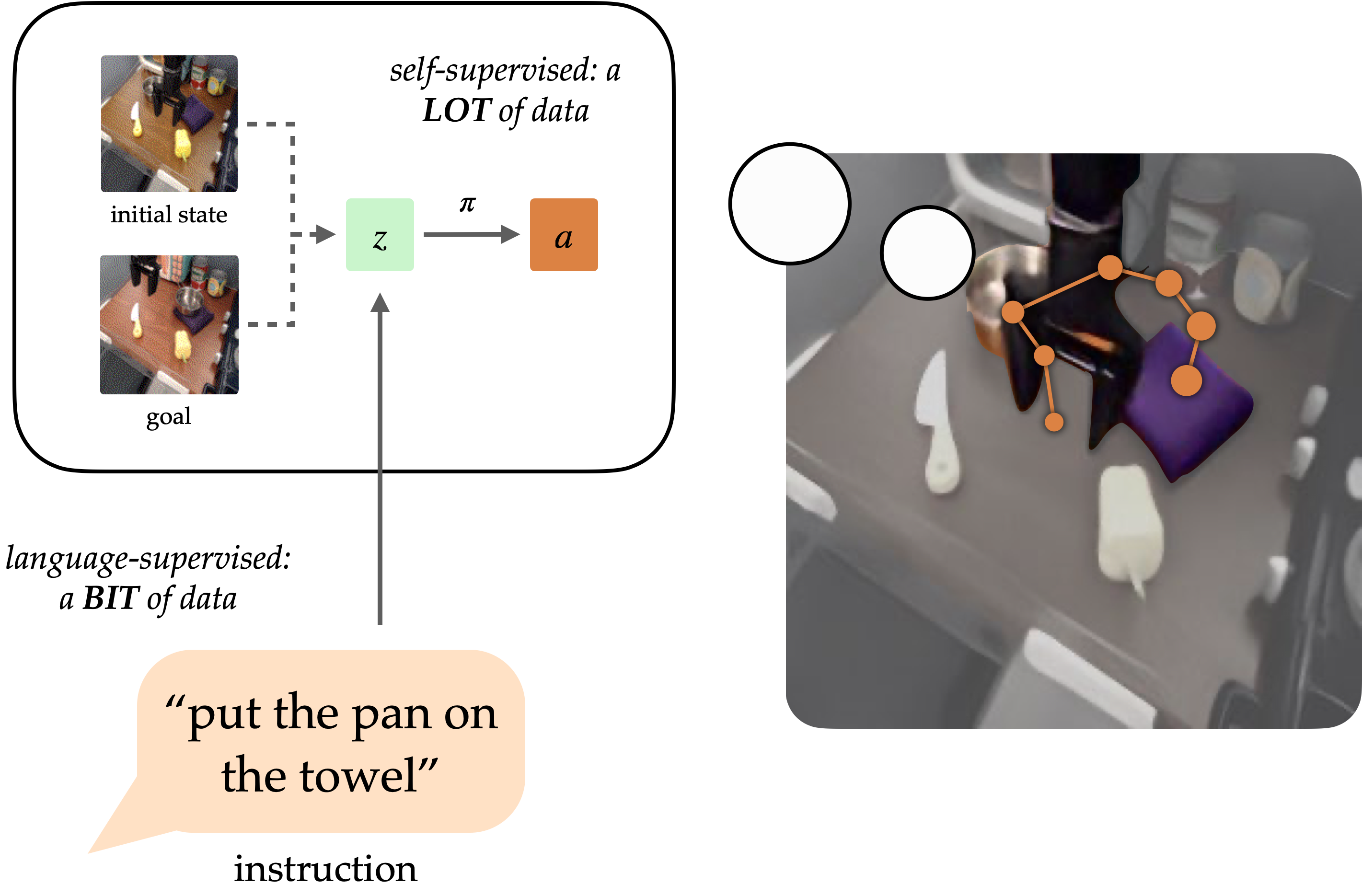
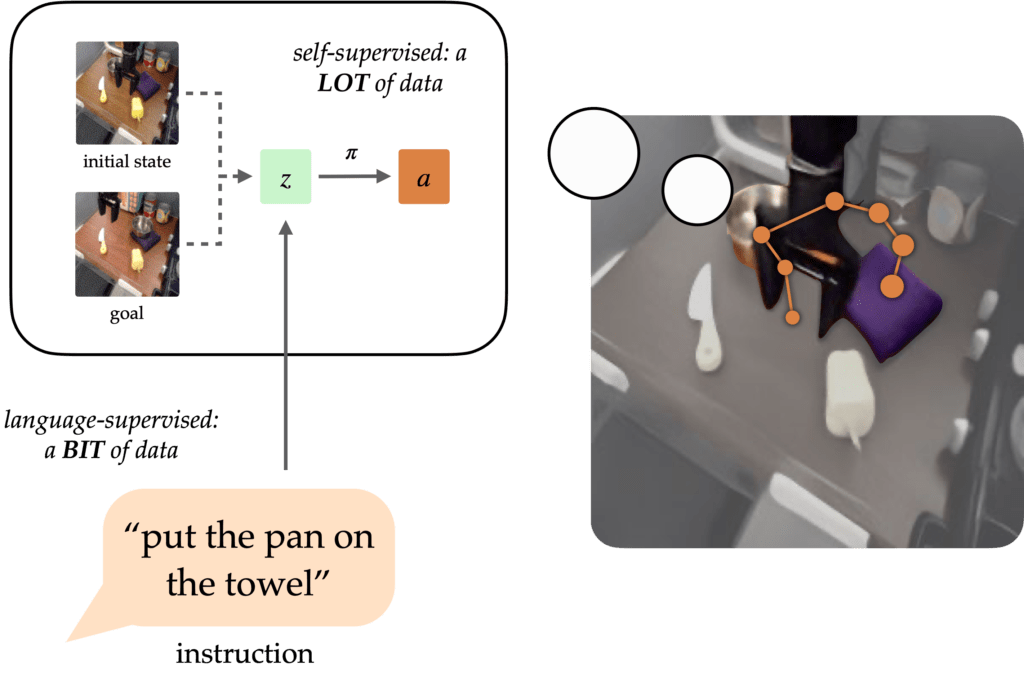
A longstanding goal of the field of robot learning has been to create generalist agents that can perform tasks for humans. Natural language has the potential to be an easy-to-use interface for humans to specify arbitrary tasks, but it is difficult to train robots to follow language instructions. Approaches like language-conditioned behavioral cloning (LCBC) train policies to directly imitate expert actions conditioned on language, but require humans to annotate all training trajectories and generalize poorly across scenes and behaviors. Meanwhile, recent goal-conditioned approaches perform much better at general manipulation tasks, but do not enable easy task specification for human operators. How can we reconcile the ease of specifying tasks through LCBC-like approaches with the performance improvements of goal-conditioned learning?